Citrulline is a non-essential amino acid that is found in abundance in the fruit that symbolises summer: watermelon. Citrulline was initially isolated from watermelon, which is where it got its very special name ("citrullus" means watermelon in Latin).
Within the body, citrulline increases the metabolic rate by acting specifically in the liver where arginine synthesises nitrogen monoxide, which forms citrulline molecules as a by-product.
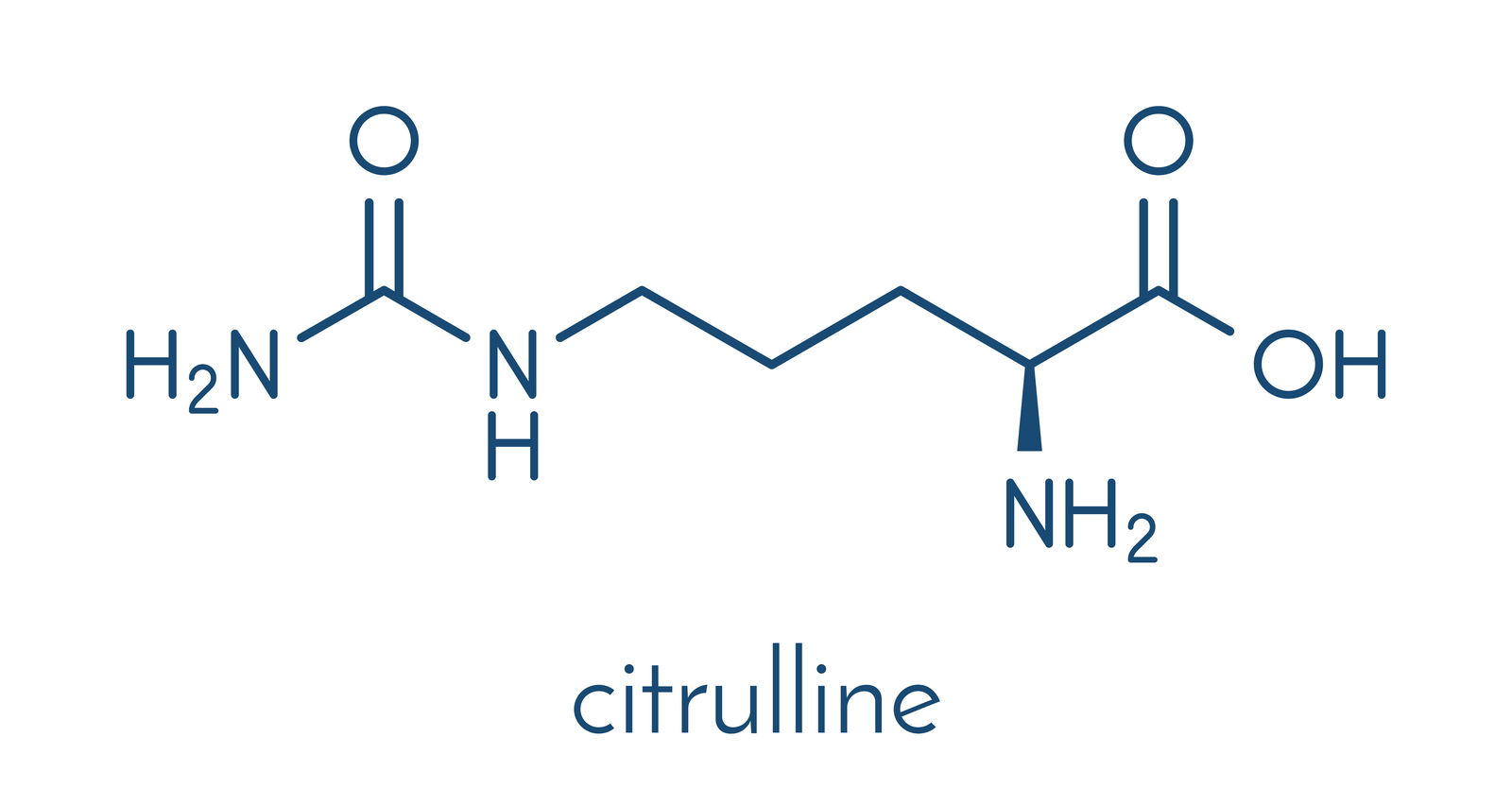
The chemical formula of Citrulline is C6H13N3O3
Through these processes, the amino acid enters the urea cycle in the liver: a fundamental process for the elimination of nitrogenous wastes (urea), such as ammonia.
This substance is extremely toxic to the body and, if accumulated, it creates a feeling of premature fatigue during aerobic or anaerobic activity, which increases its production.
What does citrulline do?
First and foremost, citrulline is known to the public as the "aphrodisiac amino acid" due to its interesting vasodilatory properties that may facilitate an erection, but the molecule's properties do not end there.
· Increased arginine
L-Citrulline supplements are very useful for increasing levels of arginine in the blood, making it available for the synthesis of nitric oxide and the other functions associated with it.
Several studies have shown that with the same dose and method of administration (oral), L-citrulline results in increased blood arginine levels, almost twice as high as the same dose of sustained-release arginine, even 20% higher than the same dose of immediate-release arginine.
· Dilatation and the protection of blood vessels
When the amino acid is transformed into arginine, it creates a noticeable vasodilatory effect by stimulating the cardiovascular system, improving the elasticity of blood vessels and providing an anti-arteriosclerotic effect.
Induced vasodilation is used in the medical field to alleviate erectile dysfunction and improve athletic performance by increasing the blood supply and, consequently, the supply of oxygen and essential nutrients to tissues engaged in effort, increasing the body's metabolic rate.
· Recovery from psychophysical stress
Taking sufficient amounts of citrulline has been proven to help improve physical and mental performance, especially if you have an active and hectic lifestyle.
· Enhancing aerobic performance
L-citrulline is often found salified with malic acid to produce citrulline malate which aims to increase the ergogenic effects to improve physical performance.
Inside the body, citrulline malate leads to an increase in bicarbonate levels, an acid that carries out a buffering function by absorbing lactic acid molecules.
In particular, a French study found that taking citrulline malate before aerobic activity leads to a significant reduction in fatigue and a 34% increase in ATP production during activity, with a 20% increase in PCR recovery after training.
Athletes in high-intensity sports featuring prevalently aerobic mechanisms, such as boxers, footballers, basketballers, runners, cyclists, etc., can benefit greatly from citrulline malate supplementation.
Which foods contain citrulline?
Good doses of citrulline are found in watermelon and its relations: yellow melon, green melon and cucumber.
It is also present in other fresh and dried fruits and vegetables, such as apples, pumpkin, courgettes, garlic, onion, almonds, walnuts, hazelnuts, chickpeas, and soy.
High quantities are also present in animal livers.

Watermelon and melon are naturally rich in citrulline
Contraindications and warnings
When there is a deficiency of the enzyme required to catalyse the citrulline-arginine reaction of the urea cycle, a disease called citrullinemia may develop, leading to the formation of ammonia in the blood.
Some studies indicate that zinc supplements can improve the conversion of citrulline - arginine in the liver and, at the same time, maintain low levels of NH3 in the blood.
Citrulline promotes the use of three essential branched-chain amino acids (BCAA: Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine) as an energy source, reducing serum concentrations during prolonged exercise.
Dosage and intake method:
To take advantage of the ergogenic effect of citrulline malate, it is advisable to start taking 6 grams and, after assessing the effects (excessively high doses can cause nausea and abdominal pain), you can switch to 8 grams.
Citrulline must be taken approximately 15-30 minutes before or also during training to benefit from a more diluted action during exercise.
(Updated content)
