Life sometimes makes us live moments of great stress and anxiety, on the one hand asking us to face situations of physical or mental discomfort, on the other to constantly increase our performances to keep up with a thousand commitments and objectives.
However, what we often overlook is the effect that the stress hormone, cortisol, has on our body. So let's see what is stress, the symptoms of high cortisol, the link with sport and how to lower cortisol with the support of specific supplements.
High cortisol and stress

When the cortisol levels rise, the symptoms of stress appear.
Cortisol is physiologically produced by the body in the fasciculated area of the cortical portion of the adrenal glands by the ACTH hormone created by the pituitary gland. It is a steroid hormone, that is, which derives from cortisone, which plays an important role in many positive phenomena in our body. Stress can be divided into two basic categories:
- Eustress. Intended as "positive stress", it represents the psychophysical stimulus that we need to face and contrast an event that balances homeostasis.
- Distress. This is the "negative stress" that results in the unpleasant symptoms for the individual that often leads to the full-fledged presence of pathologies.
The stress hormone is not to be demonized per se because it allows a series of fundamental functions for our survival!
Positive effects of cortisol
- Speeds up the metabolism.
- It improves the reactive ability of possible dangers.
- It increases blood pressure by preparing the muscles for action through the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- Restores glucose levels during long periods of fasting.
- It lowers the level of inflammation caused by an uncontrolled immunological reaction. If the body develops an infection, the immune system begins to counteract the inflammatory process by becoming hyperactive. Cortisol, therefore, lowers the number of lymphocytes to restore the body's balance (homeostasis)
Without this hormone life would not be possible but, like all hormonal secretions, it can also have negative effects resulting from a possible hyper-production, the so-called high cortisol, which leads to states of psychophysical stress accompanied by anxiety, palpitations, increased sweating, a sense of fatigue and all those unpleasant symptoms that we know well and that we will see in detail now.
Negative effects of stress on health
The excessive production of the stress hormone derives from the most varied situations in which the individual starts spontaneously producing cortisol in much larger quantities than normal.
Symptoms of high cortisol
- Difficulty sleeping. Cortisol levels drop significantly during sleep to allow the body to relax, but when the secretion mechanism changes you can start to suffer from insomnia.
- Chronic fatigue. Since you sleep badly, a state of chronic fatigue is established due to the inability to recover the lack of accumulated rest.
- Junk food cravings. High cortisol increases the production of sugar in the blood, therefore there will be an increase in insulin and consequent insulin resistance. Hyperinsulinemia will lead the subject in a short time to desire high-calorie foods rich in fats and carbohydrates.
- Weight gain. Cortisol inhibits the possibility of exploiting the energy reserves that come from fats, continuing to accumulate the lipids introduced in the diet.
- Frequent flu and colds. High levels of this hormone deactivate the body's natural self-repair mechanisms, affecting the functioning of the thymus gland, whose activity consists in maturing various types of lymphocytes capable of recognizing and destroying infected cells. This leads to a weakening of the immune system which leaves us vulnerable to disease.
- Catabolism. In situations of prolonged fasting, cortisol demolishes the amino acid structure to obtain energy and nutrients.
Stress and overtraining

Sportsmen also suffer from stress: overtraining syndrome.
We often see an excess of cortisol in professional athletes, because even particularly intense and repeated physical training over time prostrates body and mind leading to the so-called overtraining syndrome, a condition recognizable due to a series of well-defined symptoms that affect the athlete, in particular during the preparation periods for competitions and competitions.
Symptoms of overtraining syndrome
- repeatedly poor performance, without explanation,
- fatigue, muscle pain, depression,
- increased vulnerability to infections and gastrointestinal complaints,
- sleep disturbance and weight loss,
- overload injury,
- increased resting heart rate and blood pressure,
- changes in the hematocrit,
- changes in the hemoglobin rate,
- a decrease in testosterone level,
- modification of the testosterone/cortisol ratio in favor of the latter.
In these cases it will be necessary for the coach to put the athlete's health before the preparation needs, reducing the loads and the volume of training to restore adequate hormonal levels. It is recommended to resume training at full speed only when the symptoms have disappeared.
How to lower cortisol
Lowering stress levels is possible first of all by trying to focus on what we can control: our mind.
When stress grips us, we focus on one action at a time, what we are doing here and now, so as not to get caught up in the anxiety of the situation and keep under control the irrational and excessive reactions of our mind. Closing your eyes, taking a few breaths, concentrating on our sensations and interrupting the loop of thoughts is fundamental for lowering stress peaks!
On a physical level, it is important to intervene with a constant and moderate exercise program, a balanced diet and the support of specific supplements, to contribute on several fronts to eliminate insulin resistance and decrease the circulating cortisol.
Some supplements act on the modulation of the circadian rhythms of cortisol helping to keep them under control.
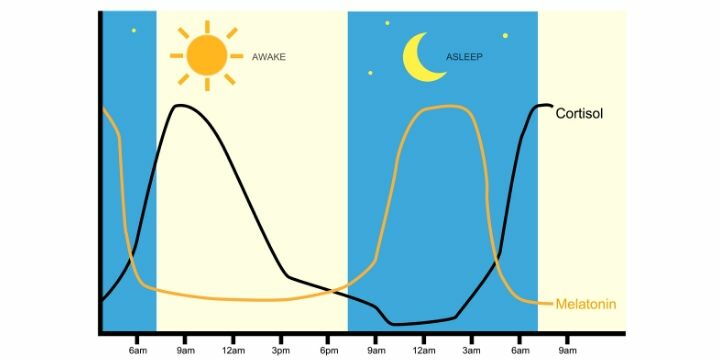
Circadian changes in cortisol (stress) and melatonin (sleep hormone) levels.
As seen in the graph, the stress hormone undergoes several circadian variations and reveals rather high peaks at the beginning of the day between 6.00 and 9.00 in the morning. It would, therefore, be better to take our anti-stress supplements in the morning, to counteract the rise of cortisol during the rest of the day.
Supplements against stress
Here are some natural products that, through the synergy of several beneficial plant extracts, can help regulate the action of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine to reduce the effects of psychophysical stress and, therefore, lower cortisol levels:
- Ashwagandha: calming plant capable of increasing fatigue tolerance, endurance, concentration, and mental focus.
- Rhodiola Rosea: natural tonic whose roots are appreciated for the powerful energizing anti-stress effects, able to support memory and learning.
- Berberine extract: helps to optimize the transport of glucose, directing it within the muscles, improving insulin sensitivity, the use of fatty acids and reducing the blood levels of triglycerides.
