Our body spontaneously produces vitamin D due to the effect of sunlight on the skin and, precisely because it originates inside the body, according to current definitions, this very important substance is both a vitamin and a hormone. Let's deepen our knowledge of vitamin D and find out why it is so important for our health!
Vitamin D in food

There are two main food sources of vitamin D:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is the one most often added to food (such as milk) and is the form most used in food supplements;
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Vitamin D in food is naturally found in good quantities in the following foods 5:
- cod liver oil;
- fish (mackerel, sardines, salmon, herring, swordfish, tuna);
- butter and whole yogurt;
- egg yolk;
- dark green leafy vegetables (chard, chicory, broccoli, black cabbage and curly).
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency causes rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Rickets, characterized by the body's inability to calcify the bone matrix, the provoking of a softening of the bones of the skull, the flexing of the bones of the legs, the curvature of the vertebral column and the increase in the size of the joints.
Although once common, these pathologies are fortunately extremely rare today. Vitamin D deficiency is currently found mainly among the elderly who do not expose themselves enough to the sun, especially among those who live in rest homes. The consequences are:
- lack of strength,
- bone density reduction,
- joint pain (1).
Benefits of Vitamin D
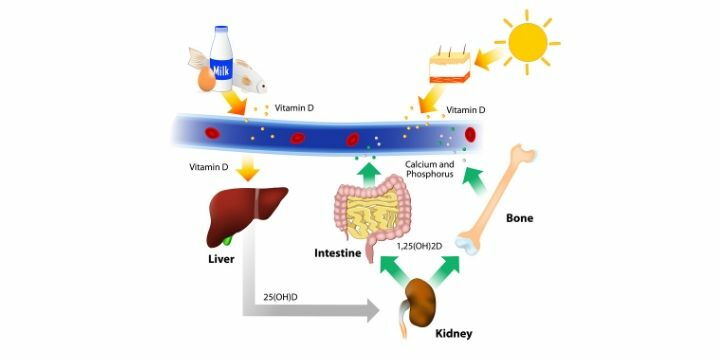
Vitamin D is known in particular for its ability to stimulate the absorption of calcium. However, there are various forms of D vitamins, each of which exerts a different level of activity on calcium metabolism.
In the skin, sunlight transforms the precursor of vitamin D (7-dehydrocholesterol) into vitamin D3, which is then transported to the liver and converted by an enzyme into 25-hydroxycholecalciferol or 25 (OH) D. In the kidneys, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol is subsequently converted by other enzymes into the more "active" form of vitamin D3, which participates in the mineralization and compactness of bones and teeth, promoting the absorption of calcium and intervening in the health of muscles and immune system.
Vitamin D also appears to exert actions that help keep cancer cells in check, especially in the case of colon and breast cancers (3-6). The incidence of colon and breast cancer is higher in areas where exposure to sunlight is lower.
Liver, kidney and osteoporosis disorders interfere with the conversion of cholecalciferol into more potent vitamin D compounds, preventing the conversion to the most active final form of the vitamin. Researchers have proposed many theories to explain this diminished conversion, including a relationship with estrogen and magnesium deficiency. Boron trace mineral has recently been speculated to play a role in this conversion.
Available forms
As we have seen, vitamin D2 is the most common form of nutritional supplement.
Calcitriol, the pharmacological form (which requires a prescription) of vitamin D, is about ten times more potent than vitamin D2 or D3. Doctors prescribe calcitriol especially for patients with kidney problems, as they are unable to convert vitamin D into its most active form.
Main uses

The main use of vitamin D supplements is the prevention of vitamin D deficiency itself, which could occur in people who follow a vegan diet since this vitamin is found almost exclusively in the food of animal origin.
Night shift workers, dark-skinned people who have little exposure to sunlight and those suffering from intestinal, kidney or liver diseases are also at risk of shortages.
Specific dosages
The recommended daily dose is between 200 and 400 IU. For older people who are not exposed to sunlight or who live in the northernmost latitudes, a higher daily intake of 400-800 IU is recommended.
However, it is not recommended to give supplements over 400 IU per day in most adults, young children and adolescents.
Warnings and precautions
Vitamin D, of all vitamins, is potentially the most toxic. Dosages higher than 1000 IU per day are not recommended because too much vitamin D could lead to an increase in the concentration of calcium in the blood (potentially serious condition), deposition of calcium in the internal organs and kidney stones.
Several researchers suggest that prolonged hyper-consumption of vitamin D in enriched foods contributes to arteriosclerosis and heart disease, probably as a result of reduced magnesium absorption (7).
Interactions
Vitamin D is complexly linked to calcium metabolism. Colestyramine, diphenylhydantoin, phenobarbital and mineral oils interfere with the absorption and / or metabolism of vitamin D.
Sources
- Gloth FM and Tobin HD, Vitamin D deficiency in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 43, 822-828, 1995.
- Lore F, Nuti R, Vattimo A, and Caniggia, Vitamin D metabolites in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Horm Metabol Res 16, 58, 1984.
- DeLuca HF, The vitamin D story: A collaborative effort of basic science and clinical medicine, FASEB J 2, 224-236, 1988.
- Pols HAP, et al., Vitamin D: A modulator of cell proliferation and differentiation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 37, 873-876, 1990.
- Reicher H, Koeffler HP, and Normann AW, The role of vitamin-D endocrine system in health and disease. New Engl J Med 320, 980,981, 1989.
- Garland CF and Garland FC, Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likehood of colon cancer? Int J Epidemiol 9, 227-231, 1980.
- Seeling MS, Magnesium deficiency with phosphate and vitamin D excess: Role in pediatric cardiovascular nutrition. Cardio Med 3, 637-650, 1978.
